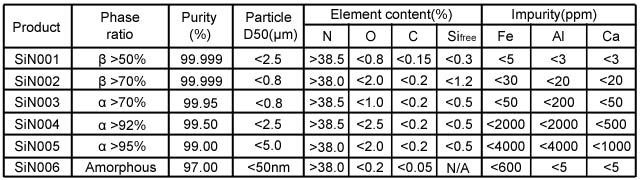
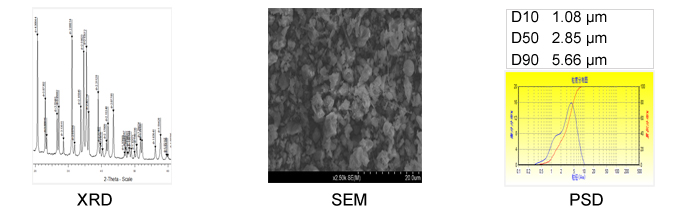
Silicon Nitride




Molecular Formula:Si3N4 CAS: 12033-89-5 Density:3.17g/cm3 Color: Grey Refractivity:2.016 Solubility in water: Insolubility | Si3N4 has excellent high thermal stability ,thermal shock resistance and high resistivity. It is very hard(8.5 on the mohs scale), and can only corroded by dilute HF and hot H2SO4. Silicon nitride also has other structural components, such as Si2N,SiN and Si2N3,which are stoichiometric phases. |

There exist three crystallographic structures of silicon nitride (Si3N4), designated as α, β and γ phases. The α-Si3N4 is low-temperature phase (can be produced at temperatures 1350-1450℃), and it would transform into β phase when temperature is above 1500℃.The α and β phases are always symbiotic, the γ phase can only be synthesized under high pressures and temperatures.

1. The material is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen environment. With an iron catalyst, the reaction rate will be accelerated and can be completed in a few hours.
3 Si + 2 N2→Si3N4
2. SiCl4 and ammonia were used to produce iminodium silicon at low temperature and then decomposed to ultrafine Si3N4 at high temperature.
SiCl4(l)+6 NH3(g)→Si(NH)2(s)+4 NH4Cl(s) at 0℃
3 Si(NH)2(s)→Si3N4(s)+N2(g)+3 H2(g) at 1000℃
3. Carbon powder was added with SiO2, which was first reduced in nitrogen atmosphere and then nitrided to form Si3N4. The carbothermal reduction was the earliest used method for silicon nitride production and is now considered as the most-cost-effective industrial route to high-purity silicon nitride powder.
3 SiO2+6 C+2 N2→Si3N4+6 CO
4. Electronic-grade silicon nitride films are formed using chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The raw materials are usually silane and ammonia, which react to form silicon nitride films. The silicon nitride films prepared by LPCVD and PECVD techniques are porous amorphous.
3 SiH4(g)+4 NH3(g)→Si3N4(s)+12 H2(g)
3 SiCl4(g)+4 NH3(g)→Si3N4(s)+12 HCl(g)
3 SiCl2H2(g)+4 NH3(g)→Si3N4(s)+6 HCl(g)+6 H2(g)

If a certain flux is added, the silicon nitride ceramics can be sintered at a lower temperature. Discharge Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a very effective sintering method. Because the sintering process takes only a few seconds, the sintering of ceramic parts can be realized by SPS in the range of 1500-1700 ℃.
The reason why silicon nitride ceramics are not widely used is because of the high cost, not the performance. For example, the performance of silicon nitride bearings has outperformed that of metal bearings, and their cost reduction and increase of market share show a regular inverse ratio.
1.Automobile engine parts
2.High-end bearings
3.High temperature resistant parts of immersion heater
4.Human medical replacement parts
5.Cutting tool
6.Electronic shielding material
7.IGBT
8.Phase Change Thermal Storage Porous Ceramics
9.Mssile-borne radome
10.Ceramic manned capsule for deep-sea exploration
11.Thermal conduction substrate
12.Solar polysilicon crucible

- Barium Nitride
- Vanadium Nitride
- Molybdenum Nitride
- Copper Nitride
- Cobalt Nitride
- Titanium Nitride
- Yttrium Nitride
- Terbium Nitride
- Praseodymium Nitride
- Manganese Nitride
- Chromium Nitride
- Gadolinium Nitride
- Dysprosium Nitride
- Erbium Nitride
- Cerium Nitride
- Iron Nitride
- Lanthanum Nitride
- Gallium Nitride
- Ytterbium Nitride
- Calcium Nitride
- Europium Nitride
- Strontium Nitride
- Aluminum Nitride
- Silicon Nitride




